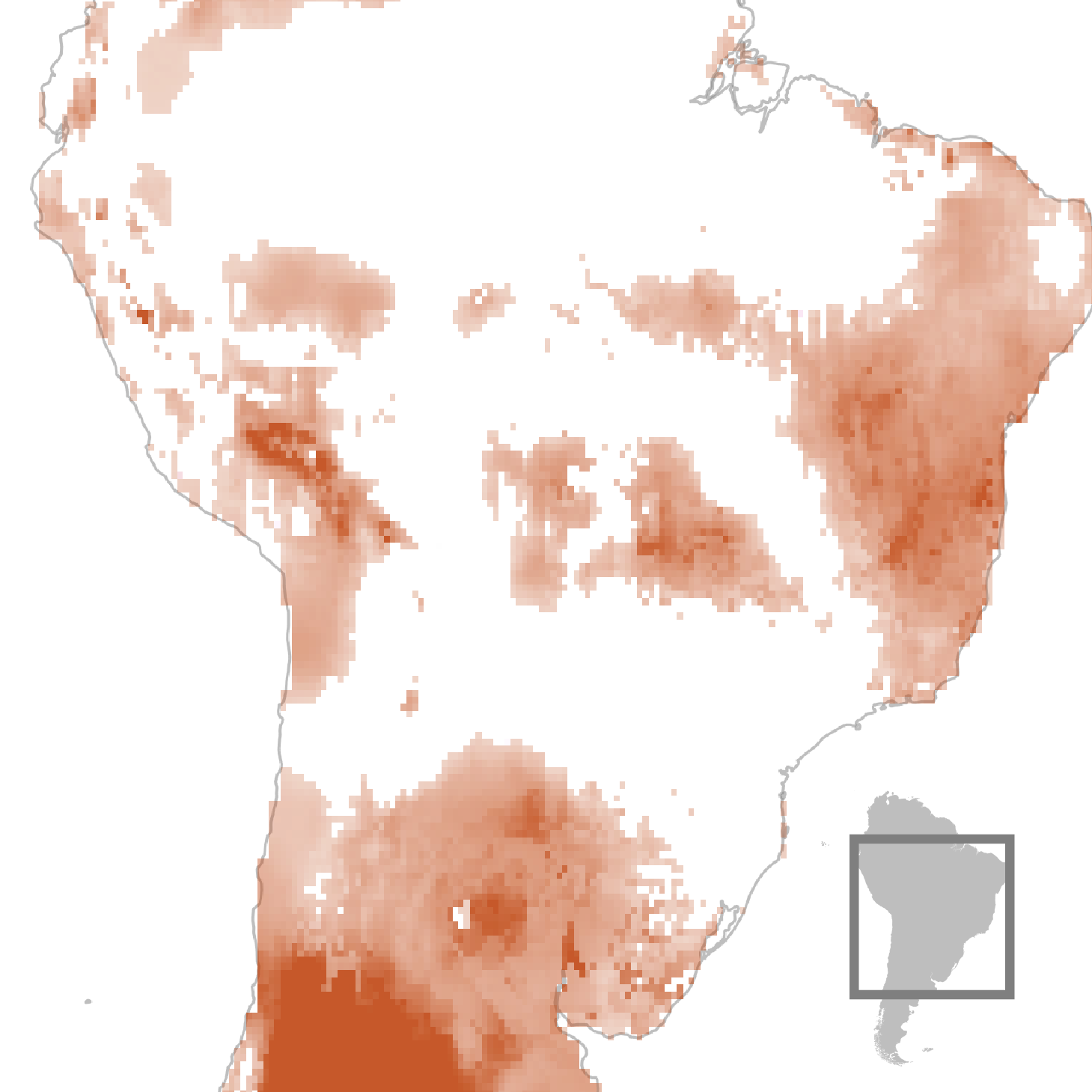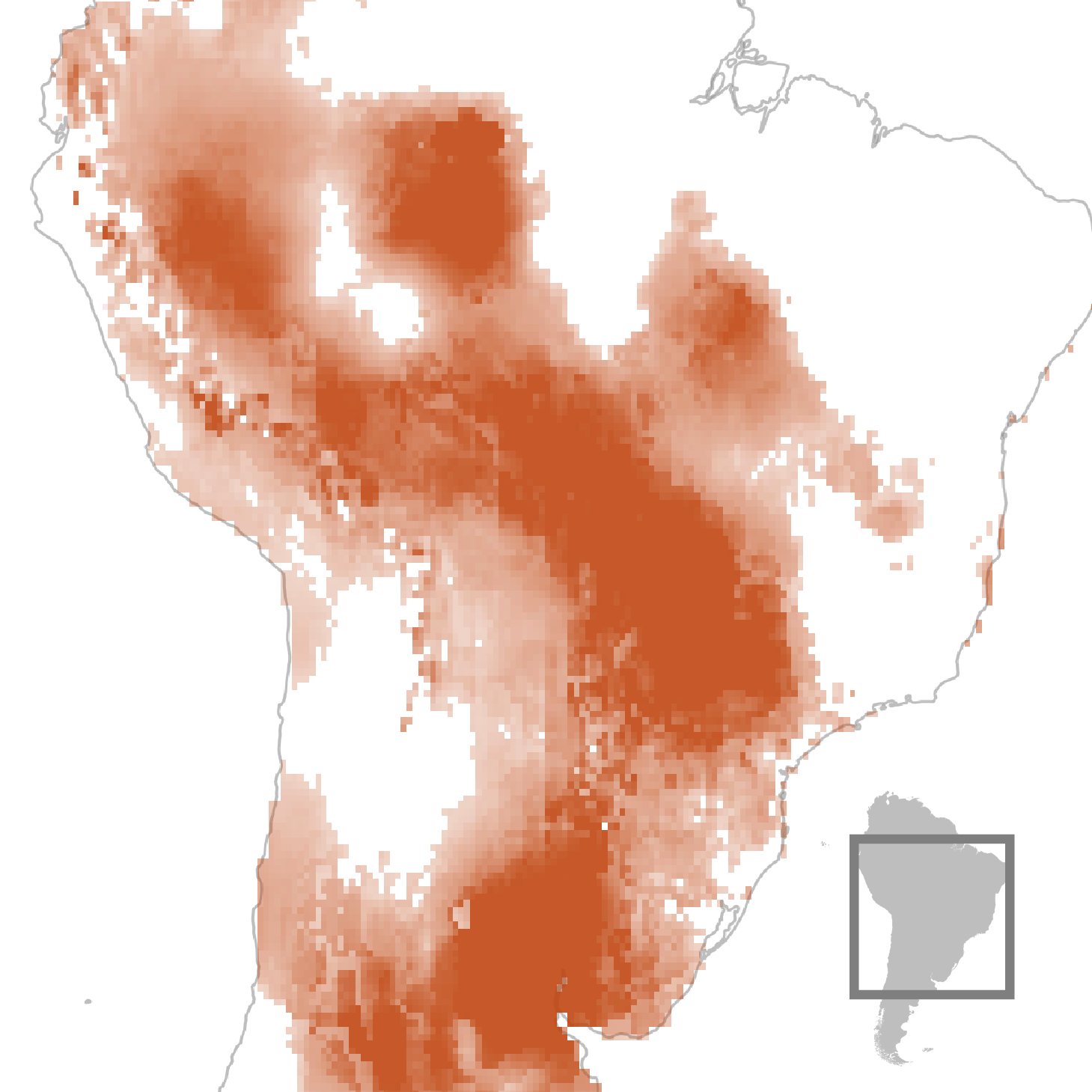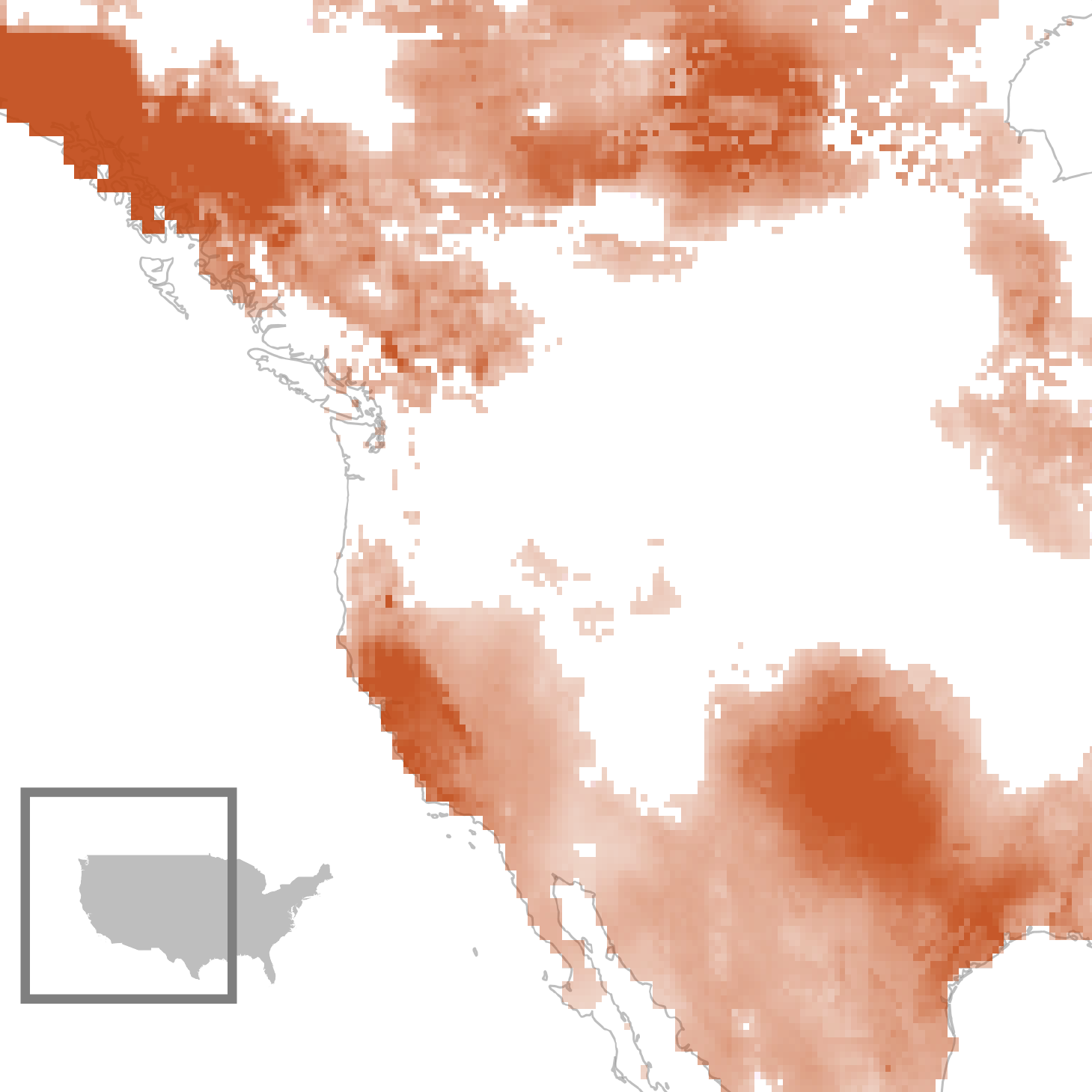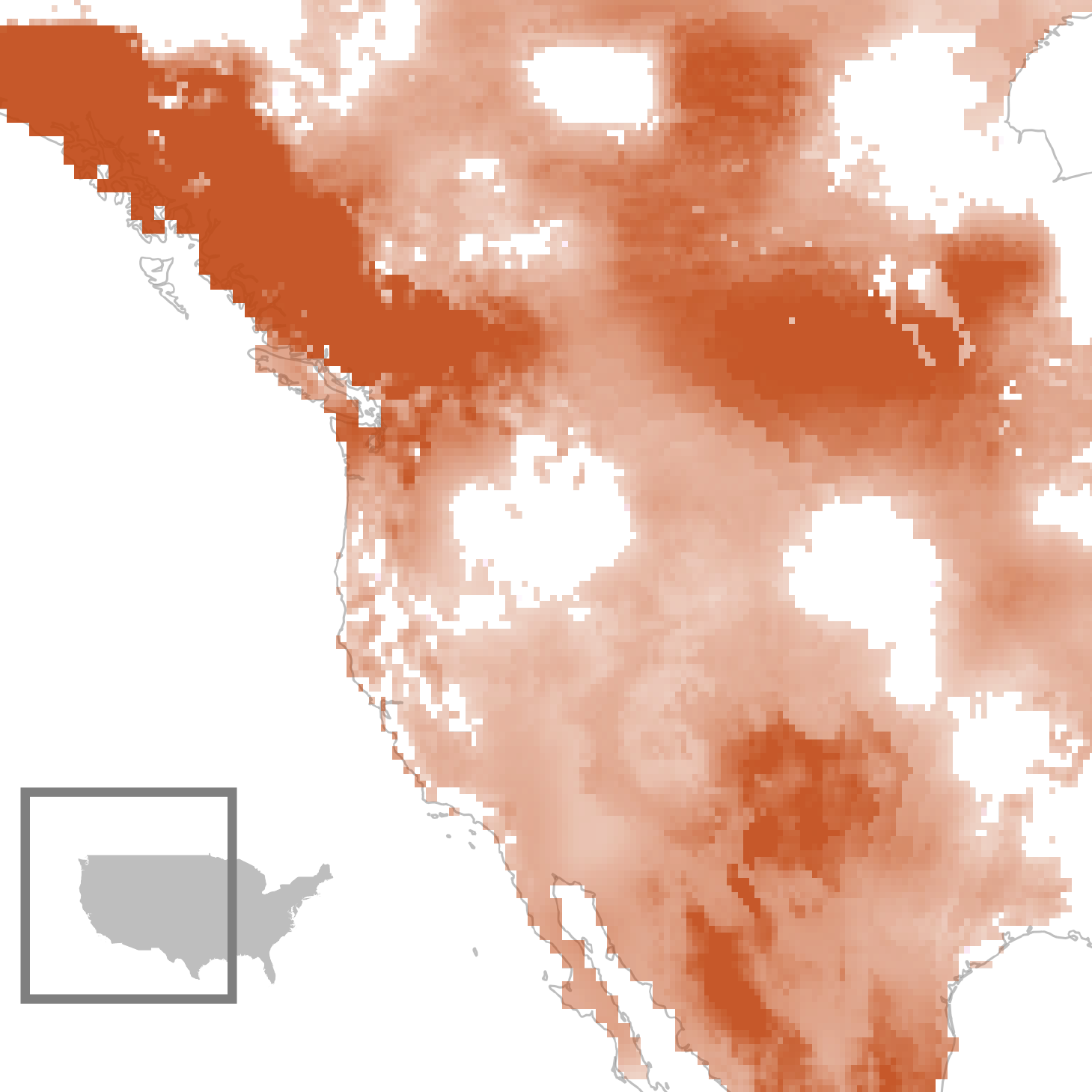
Because the planet will get warmer and its reservoirs shrink and its glaciers soften, folks have more and more drilled right into a in large part ungoverned, invisible cache of clean water: the huge, hidden swimming pools discovered deep underground.
Now, a brand new find out about that examines the sector’s general provide of clean water — accounting for its rivers and rain, ice and aquifers in combination — warns that Earth’s maximum very important useful resource is instantly disappearing, signaling what the paper’s authors describe as “a crucial, rising risk to humanity.” The landmasses of the planet are drying. In maximum puts there may be much less precipitation whilst moisture evaporates from the soil quicker. Greater than the rest, Earth is being slowly dehydrated via the unmitigated mining of groundwater, which underlies huge proportions of each and every continent. Just about 6 billion folks, or 3 quarters of humanity, are living within the 101 international locations that the find out about recognized as confronting a internet decline in water provide — portending huge demanding situations for meals manufacturing and a heightening chance of war and instability.
The paper “supplies a glimpse of what the longer term goes to be,” mentioned Hrishikesh Chandanpurkar, an earth programs scientist running with Arizona State College and the lead writer of the find out about. “We’re already dipping from a accept as true with fund. We don’t in fact know the way a lot the account has.”
The analysis, printed on Friday within the magazine Science Advances, confirms no longer simply that droughts and precipitation are rising extra excessive however studies that drying areas are speedy increasing. It additionally discovered that whilst portions of the planet are getting wetter, the ones spaces are shrinking. The find out about, which excludes the ice sheets of Antarctica and Greenland, concludes no longer handiest that Earth is struggling an epidemic of “continental drying” in decrease latitudes, however that it’s the uninhibited pumping of groundwater via farmers, towns and companies around the globe that now accounts for 68% of the full lack of recent water in the ones spaces, which most often don’t have glaciers.
Groundwater is ubiquitous around the globe, however its high quality and intensity range, as does its attainable to be replenished via rainfall. Main groundwater basins — the deep and regularly high quality aquifers — underlie kind of one-third of the planet, together with kind of part of Africa, Europe and South The us. However lots of the ones aquifers took thousands and thousands of years to shape and would possibly take 1000’s of years to replenish. As a substitute, a good portion of the water taken from underground flows off the land via rivers and directly to the oceans.
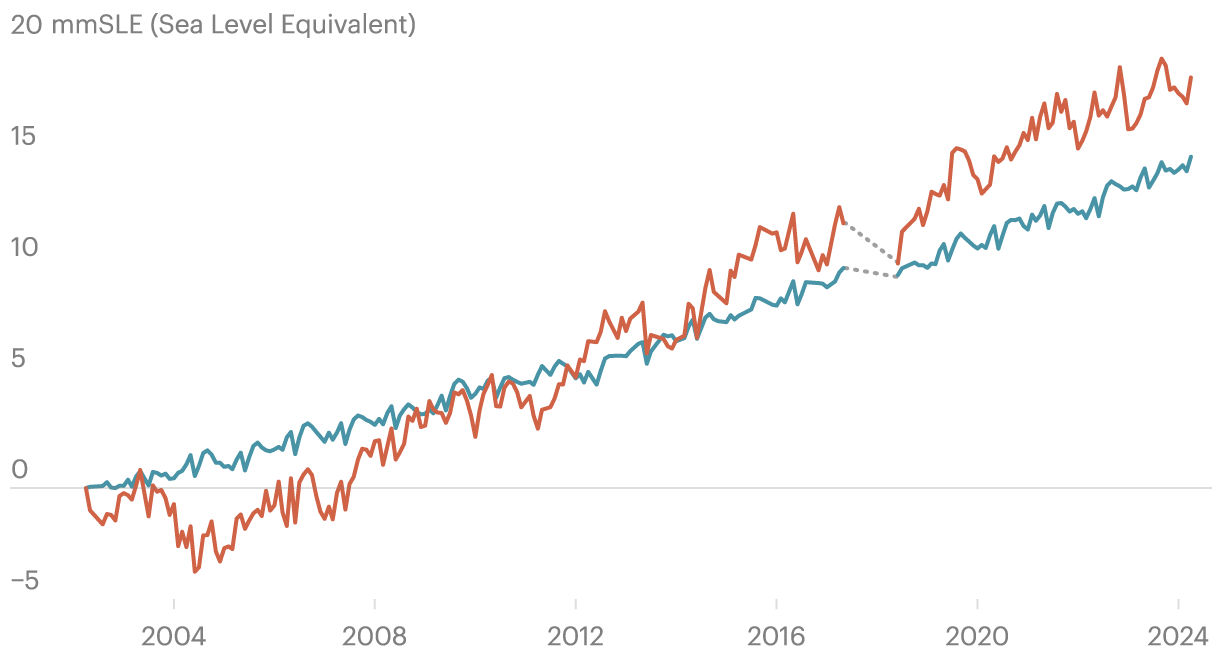
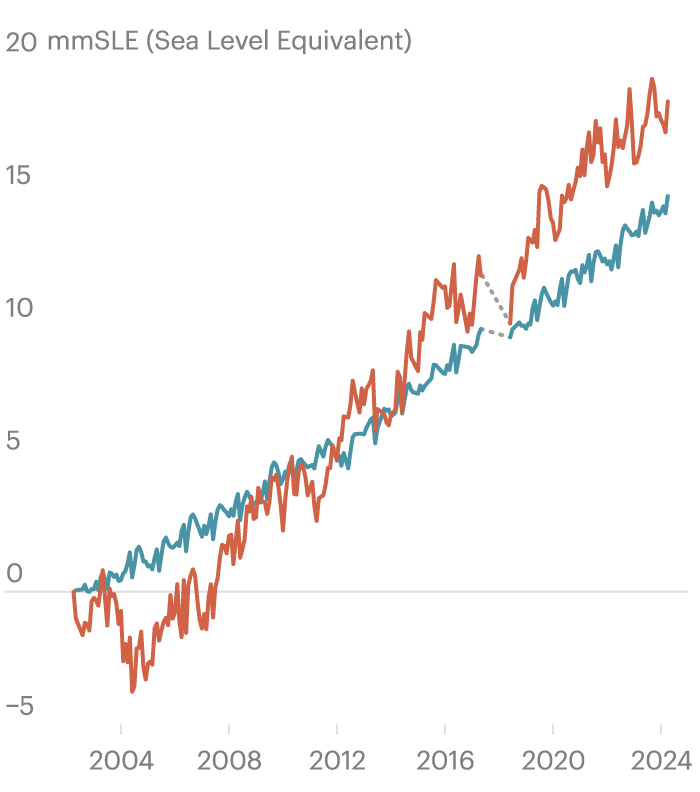
The researchers had been shocked to search out that the lack of water at the continents has grown so dramatically that it has turn out to be one of the vital greatest reasons of worldwide sea stage upward push. Moisture misplaced to evaporation and drought, plus runoff from pumped groundwater, now outpaces the melting of glaciers and the ice sheets of both Antarctica or Greenland as the biggest contributor of water to the oceans.
The find out about examines 22 years of observational knowledge from NASA’s Gravity Restoration and Local weather Experiment, or GRACE, satellites, which measure adjustments within the mass of the earth and feature been carried out to estimate its water content material. The methodology used to be groundbreaking 20 years in the past when the find out about’s co-author, Jay Famiglietti, who used to be then a professor on the College of California, at Irvine, used it to pinpoint the place aquifers had been in decline. Since then, he and others have printed dozens of papers the usage of GRACE knowledge, however the query has at all times lingered: What does the groundwater loss imply within the context of all the water to be had at the continents? So Famiglietti, now a professor at Arizona State College, got down to stock all of the land-based water contained in glaciers, rivers and aquifers and spot what used to be converting. The solution: the whole thing, and briefly.
Since 2002, the GRACE sensors have detected a fast shift in water loss patterns across the planet. Round 2014, despite the fact that, the tempo of drying seems to have speeded up, the authors discovered, and is now rising via a space two times the scale of California every yr. “It’s like this type of creeping crisis that has taken over the continents in ways in which no person used to be truly expecting,” Famiglietti mentioned. (Six different researchers additionally contributed to the find out about.) The portions of the sector drying maximum acutely are changing into interconnected, forming what the find out about’s authors describe as “mega” areas spreading around the earth’s mid-latitudes. A type of areas covers virtually the entire of Europe, the Center East, North Africa and portions of Asia.
Within the American Southwest and California, groundwater loss is a well-recognized tale, however over the last 20 years that scorching spot has additionally unfold dramatically. It now extends via Texas and up in the course of the southern Top Plains, the place the Ogallala aquifer is relied on for agriculture, and it spreads south, stretching all over Mexico and into Central The us. Those areas are attached no longer as a result of they depend at the similar water assets — generally they don’t — however as a result of their populations will face the similar perils of water tension: the perhaps, a meals disaster that would in the end displace thousands and thousands of folks.
“This has to function a serious warning call,” mentioned Aaron Salzberg, a former fellow on the Woodrow Wilson Heart and the previous director of the Water Institute on the College of North Carolina, who used to be no longer concerned with the find out about.
Analysis has lengthy established that individuals take extra water from underground when climate-driven warmth and drought are at their worst. As an example, all the way through droughts when California has enforced restrictions on supply of floor water to its farmers — which the state regulates — the giant agriculture enterprises that dominate the Central Valley have drilled deeper and pumped tougher, depleting the aquifer — which the state regulates much less exactly — much more.
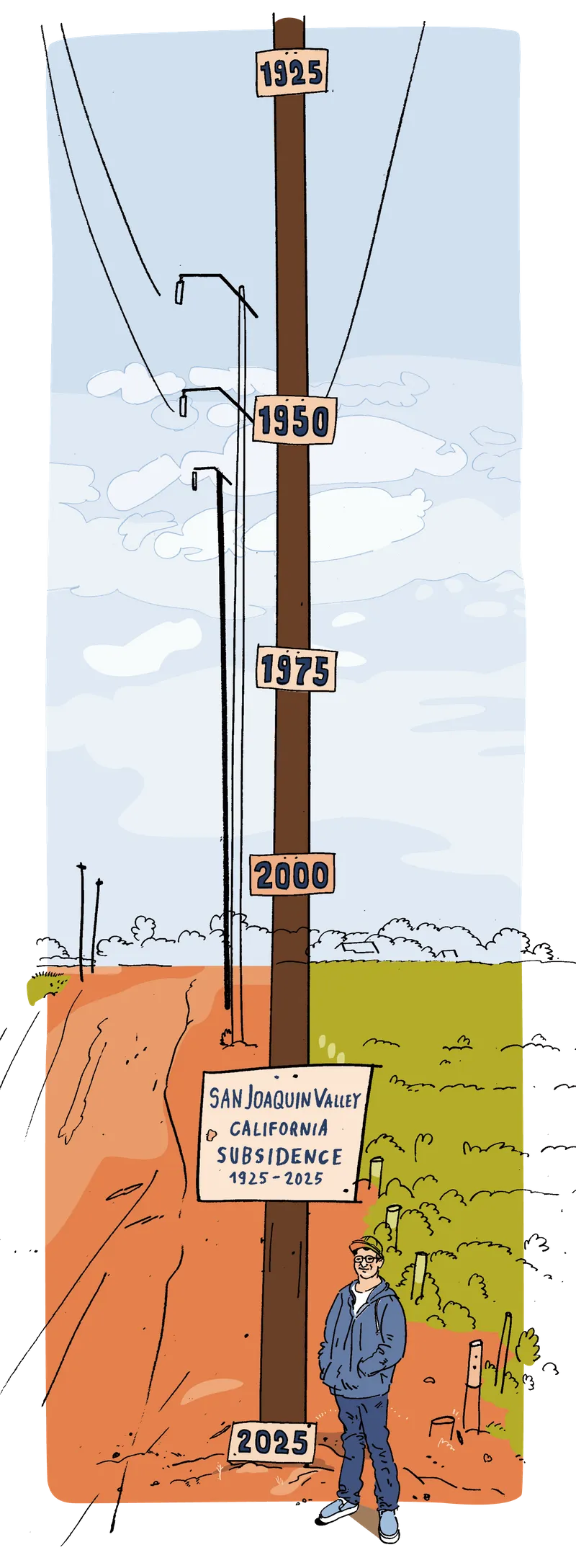
For probably the most section, such withdrawals have remained invisible. Even with the GRACE knowledge, scientists can not measure the precise ranges or know when an aquifer will likely be exhausted. However there may be one foolproof signal that groundwater is disappearing: The earth above it collapses as the bottom compresses like a drying sponge. The visual indicators of such subsidence around the globe seem to check what the GRACE knowledge says. Mexico Town is sinking as its groundwater aquifers are tired, as are huge portions China, Indonesia, Spain and Iran, to call a couple of. A fresh find out about via researchers at Virginia Tech within the magazine Nature Towns discovered that 28 towns throughout the US are sinking — New York, Houston and Denver, amongst them — threatening havoc for the whole thing from construction protection to transit. Within the Central Valley, the bottom floor is just about 30 vertical ft not up to it used to be within the first a part of the twentieth century.
When such a lot water is pumped, it has to empty someplace. Similar to rivers and streams fed via rainfall, a lot of the used groundwater makes its method into the sea. The find out about pinpoints a outstanding shift: Groundwater drilled via folks, used for agriculture or city provides after which discarded into drainages now contributes extra water to the oceans than melting from every of the sector’s greatest ice caps.
Other people aren’t simply misusing groundwater, they’re flooding their very own coasts and towns within the procedure, Famiglietti warns. That implies they’re additionally imperiling one of the crucial international’s maximum essential food-producing lowlands within the Nile and Mekong deltas and towns from Shanghai to New York. As soon as within the oceans, after all, groundwater won’t ever once more be appropriate for ingesting and human use with out dear and energy-sucking remedy or in the course of the herbal cycle of evaporating and precipitating as rain. However even then, it’s going to now not fall the place it’s wanted maximum. Groundwater “is an intergenerational useful resource this is being poorly controlled, if controlled in any respect,” the find out about states, “at super and exceptionally undervalued value to long run generations.”
That such fast and really extensive overuse of groundwater may be inflicting coastal flooding underscores the compounding risk of emerging temperatures and aridity. It signifies that water shortage and one of the crucial maximum disruptive results of weather alternate are actually inextricably intertwined. And right here, the find out about’s authors implore leaders to discover a coverage answer: Reinforce water control and cut back groundwater use now, and the sector has a device to sluggish the velocity of sea stage upward push. Fail to regulate the governance and use of groundwater around the globe, and humanity dangers surrendering portions of its coastal towns whilst pouring out finite reserves it’ll sorely want as the opposite results of weather alternate take hang.
If the drying continues — and the researchers warn that it’s now just about inconceivable to opposite “on human timescales” — it heralds “probably staggering” and cascading dangers for international order. Nearly all of the earth’s inhabitants lives within the 101 international locations that the find out about recognized as dropping recent water, making up no longer simply North The us, Europe and North Africa but in addition a lot of Asia, the Center East and South The us. This implies the center band of Earth is changing into much less liveable. It additionally correlates intently with the puts {that a} separate frame of weather analysis has already recognized as a shrinking environmental area of interest that has suited civilization for the previous 6,000 years. Blended, those findings all level to the chance of popular famine, the migration of huge numbers of folks looking for a extra strong atmosphere and the carry-on affect of geopolitical dysfunction.
Peter Gleick, a weather scientist and a member of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, lauded the brand new record for confirming tendencies that had been as soon as theoretical. The ramifications, he mentioned, may well be profoundly destabilizing. “The large overpumping of groundwater,” Gleick mentioned, “poses huge chance to meals manufacturing.” And meals, he identified, is the root for balance. The water science middle he co-founded, the Pacific Institute, has tracked greater than 1,900 incidents during which water provides had been both the casualty of, a device for or the reason for violence. In Syria, starting in 2011, drought and groundwater depletion drove rural unrest that contributed to the civil battle, which displaced thousands and thousands of folks. In Ghana, in 2017, protesters rioted as wells ran dry. And in Ukraine, whose wheat helps a lot of the sector, water infrastructure has been a widespread goal of Russian assaults.
“Water is getting used as a strategic and political device,” mentioned Salzberg, who spent just about 20 years inspecting water safety problems because the particular director for water sources on the State Division. “We will have to be expecting to look that extra regularly because the water provide disaster is exacerbated.”
India, as an example, not too long ago weaponized water in opposition to Pakistan. In April, following terrorist assaults in Kashmir, Top Minister Narendra Modi suspended his nation’s participation within the Indus Waters Treaty, a river-sharing settlement between the 2 nuclear powers that used to be negotiated in 1960. The Indus machine flows northwest out of Tibet into India, earlier than turning southward into Pakistan. Pakistan has significantly depleted its groundwater reserves — the area is going through one of the vital international’s maximum pressing water emergencies in line with the Science Advances paper. The Indus has handiest turn out to be extra very important as a provide of clean water for its 252 million folks. Permitting that water to pass the border can be “prejudicial to India’s pursuits,” Modi mentioned. On this case, he wasn’t making an attempt to recoup water provide for his nation, Salzberg mentioned, however used to be leveraging its shortage to win a strategic benefit over his nation’s foremost rival.
What’s wanted maximum is governance of water that acknowledges it as a an important useful resource that determines each sovereignty and development, Salzberg added. But there is not any global framework for water control, and just a handful of nations have nationwide water insurance policies of their very own.
The US has taken stabs at regulating its groundwater use, however in some circumstances the ones makes an attempt seem to be failing. In 2014, California handed what appeared to many a progressive groundwater control act that required communities to evaluate their general water provide and funds its long-term use. However the act doesn’t take complete impact till 2040, which has allowed many groundwater districts to proceed to attract closely from aquifers whilst they entire their plans to preserve the ones sources. Chandanpurkar and Famiglietti’s analysis underscores the effects for the sort of sluggish method.
Arizona pioneered groundwater laws in 1980, developing what it referred to as energetic control spaces the place extraction can be restricted and floor waters can be used to fill up aquifers. But it surely handiest selected to regulate the water in metropolitan spaces, leaving huge, unregulated swaths of the state the place buyers, farmers and trade have all pounced at the availability of unfastened water for benefit. Lately, Saudi buyers have pumped rural water to develop feed for farm animals exported again to the Arabian Peninsula, and hedge budget are competing to pump and promote water to cities close to Phoenix. In the meantime, 4 out of the unique 5 energetic control spaces are failing to satisfy the state’s personal goals.
“They prefer to mention, ‘Oh, the control’s doing effectively,’ however whilst you glance out on the finish of the century, there’s no water left. We tired it, and no person talks about that,” Famiglietti mentioned. “I don’t assume it’s an exaggeration to mention it’s an existential factor for towns like Phoenix.”
Each California and Arizona develop important parts of The us’s vegatables and fruits. One thing has to offer. “If you wish to develop meals in a spot like California,” Famiglietti requested, “do you simply usher in water? If we expend that groundwater, I don’t assume there’s sufficient water to truly exchange what we’re doing there.” The US would possibly no longer have a lot selection, he added, however to transport California’s agriculture manufacturing someplace a long way away and retire the land.
Chandanpurkar, Famiglietti and the record’s different authors counsel there are able answers to the issues they have got recognized, as a result of in contrast to such a lot of facets of the weather disaster, the human selections that result in the overuse of water may also be speedily corrected. Agriculture, which makes use of the majority of the sector’s recent water, can deploy well-tested applied sciences like drip irrigation, as Israel has, that sharply minimize use via up to 50%. When California farms decreased their take of Colorado River water in 2023 and 2024, the water ranges in Lake Mead, the country’s greatest reservoir, jumped via 16 vertical ft as some 390 billion gallons had been stored via 2025. Folks can cut back water waste via converting easy routines: shortening showers or taking away lawns. And towns can glance to recycle extra of the water they use, as San Diego has.
A countrywide coverage that establishes regulations round water practices but in addition prioritizes the usage of water sources for nationwide safety and a collective hobby may counterbalance the forces of dependancy and particular pursuits, Salzberg mentioned. Each and every nation wishes the sort of coverage, and if the US had been to guide, it could be offering a bonus. However “the U.S. doesn’t have a countrywide water technique,” he mentioned, relating to a disjointed patchwork of state and court docket oversight. “We don’t also have a nationwide water establishment. We haven’t idea as a rustic about how we’d even give protection to our personal water sources for our personal nationwide pursuits, and we’re a multitude.”
Information Supply: Hrishikesh. A. Chandanpurkar, James S. Famiglietti, Kaushik Gopalan, David N. Wiese, Yoshihide Wada, Kaoru Kakinuma, John T. Reager, Fan Zhang (2025). Exceptional Continental Drying, Shrinking Freshwater Availability, and Expanding Land Contributions to Sea Stage Upward thrust. Science Advances. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adx0298
Visible enhancing via Alex Bandoni. Further design and building via Anna Donlan.