To take on what is been the plastic “epidemic,” the UN spun up a committee in 2022 tasked with brokering a legally binding international settlement. This formidable treaty between UN member states used to be to handle the entire existence cycle of plastics, from manufacturing to disposal: In brief, outline what counts as plastic air pollution and curb the kinds of unchecked manufacturing that inevitably results in it. However throughout 5 classes since, international locations have failed to succeed in a consensus at the textual content.
What used to be intended to be the overall consultation ended closing yr in Busan, South Korea with out settlement, and representatives from 175 international locations are actually set to fulfill once more for section two, this time in Geneva, Switzerland. INC-5.2 will happen from August 5 to fourteen, all the way through which negotiators will try to see eye-to-eye at the issues of the draft treaty that experience so far confirmed maximum contentious. In step with the (CIEL), there are over 370 such issues.
Scope
Manufacturing, the usage of chemical substances of shock (the ones regarded as to be a possibility because of toxicity and/or different qualities), product design and the financing of treaty implementation are one of the details of confrontation. Those problems have left international locations in a impasse, in step with Cate Bonacini, Communications Supervisor for CIEL. There are international locations that argue well being must be excluded from the treaty’s scope. Those subjects shall be front-and-center going again into the talks, and UN member states have spent the closing 8 months “operating arduous in closed-door conferences to search out issues of settlement,” Bonacini mentioned in an e mail. “We’ll see the end result of that hard work quickly.”
“On the center of the problem,” Bonacini mentioned, “there’s a huge confrontation about what plastic air pollution is, and what measures are had to finish plastic air pollution.” Whilst the dedication specializes in the entire existence cycle of plastics, there may be been a lot dispute over the place that cycle in reality starts.
“As scientists, we interpret the entire existence cycle as beginning with extraction and manufacturing,” mentioned Bethanie Carney Almroth, a professor of ecotoxicology on the College of Gothenburg and a member of the Scientists’ Coalition for an Efficient Plastics Treaty. “That will be fossil fuels and uncooked plastic manufacturing all over to product, to make use of, to industry, to transportation, to waste control, mismanagement and environmental air pollution, together with remediation of current legacy plastics. It all.”
Whilst over 100 international locations closing December have been in desire of a treaty that will impose manufacturing limits, others together with adverse the caps. Forward of that consultation, the USA reportedly additionally made the verdict , in spite of previous indications that it might. Unsurprisingly, the international locations that experience taken factor with the scope of the treaty also are one of the global’s best oil manufacturers.
“There are different actors,” Carney Almroth mentioned, “which can be seeking to slim that scope to head from plastic merchandise, like water bottles, to waste control, so kind of with the exception of the outer obstacles of ways we outline the plastics existence cycle in order that it might, in essence, change into extra of a waste control treaty.”
Outdoor affect
Along with representatives from the taking part member states, scientists, environmental organizations and trade lobbyists are provide for the negotiation classes. In step with Carney Almroth, who has attended each Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC) assembly and is now in Geneva for INC-5.2, an increasing number of it is been lobbyists who take in probably the most house.
“On the closing spherical of talks, lobbyists for the petrochemical and plastics industries made up the one greatest delegation,” wrote Bangor College lecturer Winnie Courtene-Jones, who could also be a member of the Coalition, in a up to date article for . CIEL discovered that “there have been thrice extra fossil gasoline and chemical trade lobbyists than scientists” on the Busan conferences. Bonacini famous that “plastics are 99 % fossil fuels, and those corporations have a vested hobby in proceeding to generate fossil fuel-based merchandise, together with plastics.”
Their affect has performed a large function within the stalemate. They “have a large number of energy, cash and affect,” Carney Almroth mentioned, “and their lobbying efforts transcend the partitions of the negotiating house…They have got get right of entry to to resolution makers in ways in which different observers don’t.”
“They do not wish to have a look at chemical substances,” Carney Almroth mentioned. “They do not wish to have a look at manufacturing.” However that having a look at chemical substances (components, processing aids, and so on.) and manufacturing is of maximum significance, no longer handiest within the context of environmental sustainability but additionally human well being.
In a piece of writing for the in July, a bunch of scientists pointed to the a lot of possible well being results that fresh research have related to plastics, by the use of publicity to hazardous chemical substances and from micro- and nanoplastics. That incorporates an larger possibility of “more than one continual illnesses, together with most cancers, neurodevelopmental hurt and infertility” in addition to “respiration, reproductive and gastrointestinal hurt, with possible hyperlinks to lung and colon most cancers.”
The authors known as on delegates to prioritize those considerations within the upcoming negotiations and paintings towards a treaty that will finish manufacturing of poisonous chemical substances in plastics, ban the recycling of plastics containing the ones chemical substances and cut back plastic manufacturing total. Their letter comes along a separate learn about printed this summer season within the magazine that known over 4,200 chemical substances of shock in plastics, out of the 16,325 overall . The researchers argue that, on best of organising transparency across the make-up of plastics and getting rid of chemical substances of shock, plastics will have to be simplified if they will be made more secure.
The various chemical substances that move into plastics “may also be launched all through all of the plastic existence cycle, from feedstock extraction and manufacturing to make use of and waste,” the authors write. “Explicit end-of-life remedies, similar to out of control landfilling or incineration, can additional exacerbate chemical releases.” The has warned that the uncomfortable side effects at each degree within the existence cycle of plastics disproportionately hurt prone populations international, together with indigenous peoples, low source of revenue households and rural communities.
The place issues stand
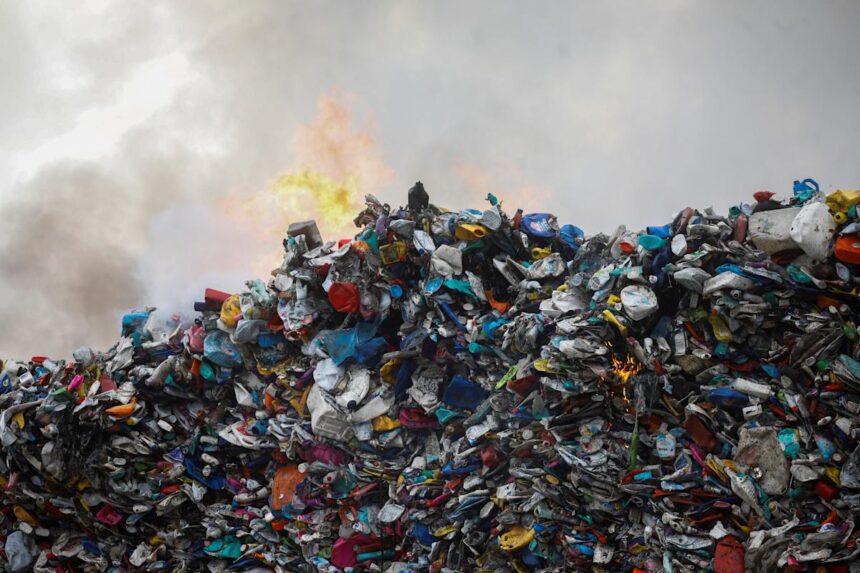
Lately, plastic is kind of inescapable — microplastics will also be now. And analysis an increasing number of suggests we are not totally conscious about how unhealthy air pollution ranges in reality are.
World plastic manufacturing has greater than doubled within the closing 25 years, with upwards of now estimated to be produced once a year. Recycled plastics make up simply 6 % of that overall, a determine that is anticipated to stick the similar whilst international plastic use and waste technology are projected to upward push 70 % via 2040, in step with the world Group for Financial Co-operation and Construction (OECD). And each and every yr, tens of thousands and thousands of heaps of plastic waste is disposed of in techniques regarded as to be environmentally unsound, finishing up in out of control dumpsites, burned overtly or collecting on land and in our bodies of water.
A printed this summer season, led via researchers from Utrecht College and the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Analysis, discovered that there is also way more plastic within the oceans than in the past concept when accounting for debris even smaller than microplastics. The workforce gathered water samples from 12 places around the North Atlantic Ocean and measured the focus of nanoplastics (plastic debris below 1 micrometer) at other depths. Through the researchers’ estimate, there might be up to 27 million metric heaps of nanoplastic within the North Atlantic by myself. That is within the ballpark of earlier international estimates for greater plastic waste throughout all the ocean.
In every other new , researchers from France’s College of Toulouse discovered we is also inhaling as much as 100 occasions extra microplastic debris indoors than earlier estimates, according to measurements of airborne microplastics within the researchers’ personal flats and automotive cabins.
The placement is pressing, particularly for prone populations, mentioned Carney Almroth. “The quantities of plastics we are generating these days and the quantity of plastic within the atmosphere are astronomical,” mentioned Carney Almroth. As of a couple of years in the past, “we had two times the mass of plastic in the world because the mass of the entire animals on land, in water, together with bugs, and now we have produced way more plastic since then.”
Plastics are “overwhelming any and all of our waste control infrastructure, so we aren’t ready to stop air pollution. We are not ready to mitigate hurt,” Carney Almroth mentioned. “The affects of plastics within the atmosphere are very huge scale, to the purpose the place they are destabilizing necessary Earth purposes like local weather, like nutrient biking, like biodiversity. After which now we have the human well being affects on best of that. It is an acute downside.”
The logistics of fending off disaster
However, because the previous 5 classes have illustrated, attaining an settlement on methods to remedy that downside is not going to be simple. The difficulty, partially, boils all the way down to how the choices are being made. Up to now, it is all being achieved via consensus reasonably than vote casting, Carney Almroth and Bonacini defined. That means lets in “a unmarried nation veto energy over choices,” Bonacini mentioned.
Petrochemical international locations together with Saudi Arabia, Russia, China, Iran, Kuwait, Qatar, India and Brazil have latched onto this, the usage of “obstructionist techniques” to pull out the negotiations. Some have insisted “with out prison foundation,” in step with CIEL, “that choices can handiest be made via consensus.” Consensus, on the other hand, is not the best choice.
The draft Regulations of Process permit for majority vote casting within the tournament a consensus cannot be reached, however whether or not that may occur is but to be observed. “There are alternatives to drive that rule,” Carney Almroth mentioned. However, a rustic (or international locations) must step up and invoke it.
At this degree of the negotiations, there’s a possibility that international locations will compromise on key provisions for time’s sake, Bonacini mentioned, which might in the long run weaken the treaty. And as soon as a treaty is finalized, “it might probably take years, if no longer many years, to make amendments to the unique textual content,” so getting it proper the primary time is the most important. Global agreements that experience taken a softer option to addressing environmental problems, just like the Paris Settlement — which shall we international locations set their very own objectives for lowering greenhouse gasoline emissions — were within the face of hastily emerging international temperatures and local weather trade.
In June on the UN Ocean Convention, representatives for 95 international locations which can be a part of the INC reaffirmed their dedication to a treaty that addresses the entire existence cycle of plastics, stages out “probably the most problematic plastic merchandise and chemical substances of shock,” improves product design to cut back environmental and well being affects and employs efficient approach of implementation. “A treaty that lacks those components, handiest will depend on voluntary measures or does no longer deal with the entire lifecycle of plastics might not be efficient to handle the problem of plastic air pollution,” the gang — which contains Canada, Australia, Colombia, Zimbabwe, the United Kingdom and Germany — wrote in . Those international locations added that “the treaty must supply for the opportunity of decision-making, via common UN procedures if all efforts to succeed in consensus were exhausted.”
If an settlement is not reached this time round, there are a selection of the way the following steps may play out. The talks might be stretched even additional into every other assembly, or international locations may come to a decision to take the subject in other places.
“Many nations are bearing in mind possible choices if negotiations fail,” Christina Dixon, Ocean Marketing campaign Lead for the Environmental Investigation Company instructed . “Choices come with returning to the United International locations Atmosphere Meeting (UNEA) to ascertain a brand new increasing mandate, growing a practice outdoor the UN for dedicated international locations to transport ahead or adopting a protocol below an current conference.” The UNEA meets subsequent in December.
We’re, as Courtene-Jones wrote in The Dialog, at “a important crossroads.” That is one thing advocates for a powerful, science-based treaty all appear to agree on. “There are a large number of puts the place we will in reality do so much to make a distinction, and fix things,” mentioned Carney Almroth. “Nations want to be formidable, and want to rise up and insist this.”