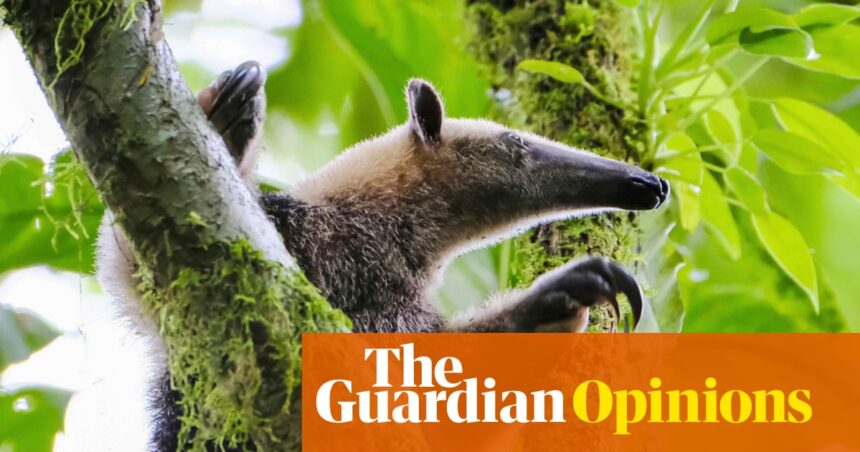
Who doesn’t love an anteater? I imply, except ants, clearly. With their lengthy snouts or even longer sticky tongues, they trundle round, slurping up bugs like milkshakes. They have got good-looking, furry tails, which they wrap round themselves at night time like a blanket. And so they’re superb folks. Large anteater moms permit their younger to hang to their backs, rucksack-style, for sessions of as much as a 12 months.
Certainly, the surrealist artist Salvador Dalí used to be so concerned with the large anteater that he as soon as took one for a stroll during the streets of Paris. And sooner than you ask, no, this wasn’t a cheese dream. There’s photographic proof.
As though that weren’t sufficient, a contemporary learn about revealed within the magazine Evolution has discovered that mammals have developed into anteaters now not as soon as, now not two times, however 12 occasions for the reason that loss of life of the dinosaurs some 66m years in the past. Anteaters, it sort of feels, are a habitual pattern. The discovering triggered the learn about’s lead creator, Thomas Vida from the College of Bonn, to inform Science mag: “Issues stay evolving into anteaters, by some means.” Which raises the query: will people in the future practice swimsuit?
Via “issues”, Vida approach mammals, and by means of “anteaters” he comprises the 4 species of anteater from Central and South The usa, the pangolins and aardvarks of Africa and Asia, and the echidnas of Australia. Other animals, on other continents, that every one observe myrmecophagy, sometimes called the intake of termites and ants. When you have been a guardian of babies, you’d name them fussy eaters. When you have been an evolutionary biologist, alternatively, you’d indicate that they’re now not being intentionally tough. As a substitute, they’ve developed to fill an excessively explicit ecological area of interest.
That area of interest is supplied by means of the arena’s intensive inhabitants of ants and termites, some 15,000 species, whose collective biomass is greater than 10 occasions higher than that of all wild mammals. A minimum of a dozen occasions in evolutionary historical past, mammals determined that if you’ll be able to’t beat them, consume them, and started to devour the crunchy delicacy.
Such an plentiful meals supply can act as what biologists name a “selective force”. Traits that enabled animals to consume extra ants and termites – and thus continue to exist higher – are much more likely to be handed on. Over tens of millions of years, animals from all 3 main teams of mammal lifestyles, together with marsupials and the egg-laying monotremes, developed to have lengthy, sticky tongues, lowered or lacking enamel and robust forelimbs for busting into insect nests.
It’s a formidable instance of convergent evolution, the phenomenon during which other species, somewhere else or occasions, independently evolve same traits. Confronted with the similar drawback – how do I consume those ants? – all of them arrived at a same resolution. So, even though they’re now not carefully comparable, they possess options which can be superficially same.
Convergent evolution is how echolocation (the facility to decide the positioning of items the use of mirrored sound) developed one after the other in bats and dolphins, camera-like eyes developed in octopuses and vertebrates, and opposable digits developed in primates, koalas and chameleons. Powered flight has developed independently a minimum of 4 occasions – in birds, bats, pterosaurs and bugs – and venom manufacturing greater than 100 occasions, whilst crustaceans have developed the vintage, crab-like frame plan a minimum of 5 occasions. Referred to as carcinisation, it has spawned crabby memes aplenty.
The evolutionary biologist Simon Conway Morris has used convergent evolution to argue that evolution is each deterministic and predictable. Rewind the tape of lifestyles, play it once more and similar-looking lifeforms would evolve, he says.
Which means in principle, with sufficient time (many tens of tens of millions of years), the semblance and retention of the considered necessary genetic mutations and, seriously, the similar selective pressures that formed the emergence of former ant-eating animals, some mammals – together with possibly us – may evolve gummy mouths and sticky tongues. Omit the historical past books, it’s the cookery books that will be rewritten.
Best there’s a fly within the ointment. We’re fallacious to presume that as a result of myrmecophagy has developed a couple of occasions, it’s the pinnacle of a few evolutionary tree. There are, in any case, many extra mammals that experience now not developed into anteaters than have began breaking into termite mounds. The truth that convergent evolution happens does now not essentially make it the default pathway.
As well as, evolution has some way of pulling the rug. It could actually be predictable, but it surely may also be quirky and erratic. In his 1989 e-book, Superb Existence, every other titan of evolutionary biology, Stephen Jay Gould, argued for the significance of random occasions. Those may also be anything else from lightning moves to asteroid affects: any unexpected incidence that derails the existing trajectory of evolution and sends it alongside a unique trail. In different phrases, “sliding doorways” moments which have been influencing evolution for so long as there was lifestyles on Earth.
So, simply because issues saved “evolving into anteaters” prior to now, doesn’t imply that historical past will repeat itself. Which is a disgrace. Anteaters and aardvarks don’t normally consume the entire ants or termites in a nest, however depart some in the back of so the colony can rebuild itself. This makes them the epitome of sustainable dwelling. If we will be able to’t evolve into them, we will be able to a minimum of be informed from them.